In fact, there are numerous cases where cancer has been successfully controlled.
This page details common cancers in dogs, their causes, symptoms, treatments, what to prepare for if your dog is diagnosed with cancer, how to cope with it, and tips for living comfortably even with cancer.
Whether your dog is about to undergo surgery or chemotherapy, is currently undergoing treatment, cannot continue treatment anymore, or has been given a terminal diagnosis, this page can be of help to you.
We also feature numerous improvement cases. We hope this can be a source of comfort and a beacon of hope for you.
目次
Symptoms That May Appear When a Dog Has Cancer
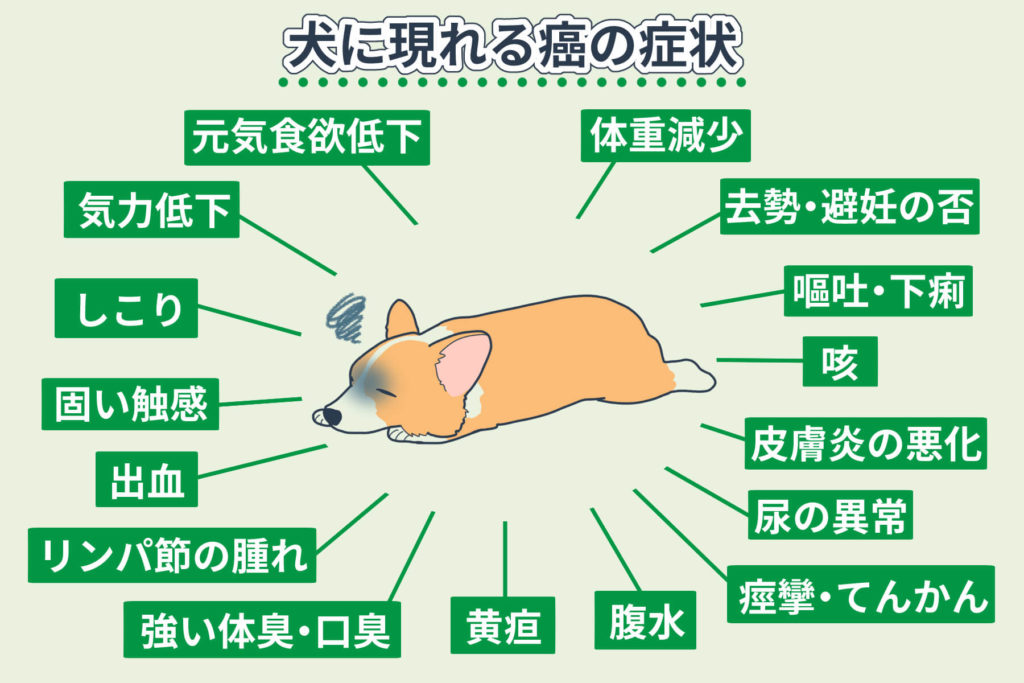
If your dog exhibits any of the following symptoms, it may be suffering from cancer.
It is recommended to visit a veterinary hospital as soon as possible to determine the cause of the symptoms showing in your dog.
Especially in advanced stages of cancer, various symptoms may appear. Please be attentive to any changes in your dog’s condition.
- Decreased energy and appetite
- Sudden weight loss
- Reduced vitality
- Palpable lumps on the body
- Hard areas when touching the body
- Bleeding from the mouth, nose, or anus
- Swollen lymph nodes
- Strong body odor or bad breath
- Not neutered or spayed
- Persistent vomiting or diarrhea
- Persistent coughing
- Worsening dermatitis
- Urination issues such as difficulty urinating, frequent urination, or blood in the urine
- Seizures or epilepsy symptoms
- Accumulation of abdominal fluid
- Jaundice
The symptoms can vary greatly depending on the location of the cancer. Below, we will explain the main types of cancer and their symptoms.
The Six Most Common Types of Cancer (Malignant Tumors) in Dogs
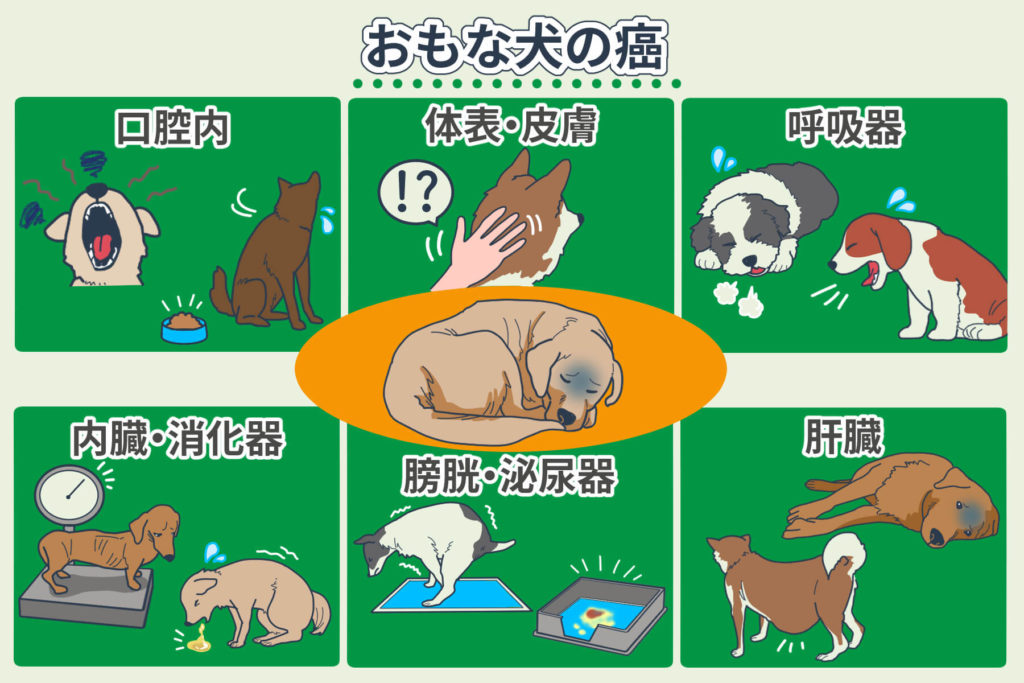
The most common types of malignant tumors (cancers) found in dogs include the following.
Oral Cancer
When cancer occurs in a dog’s oral cavity, it can lead to severe bad breath, pain, difficulty eating which results in decreased appetite, and visible changes in appearance. The main types of oral cancer include:
Some dogs may not want to show the inside of their mouths, but as the cancer progresses to advanced or terminal stages, symptoms such as being unable to eat solid foods, noticeable tumors, metastasis to the lungs causing labored breathing, and coughing may occur.
Cancer of the Body Surface and Skin
When cancer progresses, it can metastasize to the lungs or liver, leading to symptoms like coughing, fatigue, and fluid accumulation in the abdomen.
Cancers on the body surface are often noticed before they reach an advanced stage.
When cancer appears on a dog’s body or skin, you might notice a hard lump.
If you feel anything unusual while petting your dog, it is recommended to consult a veterinary clinic as soon as possible.
In addition, within the nasal cavity, conditions such as Intranasal Tumor and Nasal Adenocarcinoma in Dogs can develop.
Malignant tumors around the anus include Apocrine Gland Adenocarcinoma of the Anal Sac. Likewise, around the anus, there is a benign tumor known as Perianal Adenoma.
Respiratory Cancers
- Lung Adenocarcinoma
- Lung Squamous Cell Carcinoma
When nasal cancer develops, symptoms such as “rapid and heavy breathing,” “frequent coughing,” and “coughing up blood-tinged sputum” may appear.
Respiratory cancers may not be noticeable at first, but as they progress to advanced stages, the symptoms become severe.
If you notice any abnormalities, please visit a veterinary hospital as soon as possible.
Internal Organs and Digestive System Cancers
Symptoms such as loss of appetite, weight loss, vomiting, and diarrhea may appear. The main cancers include the following:
- Peritoneal Lymphoma
- GIST (Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumor)
- Soft Tissue Sarcoma
- Intestinal Adenocarcinoma
Additionally, if Hepatocellular Carcinoma or Liver Cancer or metastatic cancer from other organs affects the liver, it can result in diminished energy and appetite.
Incidentally, “approximately 90% of heart tumors in dogs are Hemangiosarcomas”, and Hemangiosarcoma can also develop in the spleen and liver. If these tumors grow large, they can rupture within the abdomen, leading to massive internal bleeding and potentially death.
When a dog develops a brain tumor, various symptoms can appear depending on the location of the cancer, such as “seizures,” “ataxia,” “loss of appetite,” “changes in taste,” and “vision impairment.”
Moreover, histiocytic sarcoma is an extremely malignant cancer that can lead to death within days of discovery.
It can metastasize to the liver, spleen, bone marrow, lymph nodes, brain, bones, joints, and throughout the entire body.
Osteosarcoma is a cancer that originates from bone cells called osteoblasts, and may cause symptoms such as abnormal gait and pain.
Bladder and Urinary Tract Cancer
There can be symptoms such as difficulty urinating or defecating, blood in the urine, and blood in the stool.
- Transitional Cell Carcinoma (TCC) / Bladder Cancer
- Perianal Gland Adenoma
- Apocrine Gland Anal Sac Adenocarcinoma
- Kidney Cancer
These are relevant.
Liver Cancer
In dogs, liver cancers can be either primary or metastatic, where other cancers spread to the liver. Primary liver cancers / liver tumors include:
- Hepatocellular Carcinoma
- Carcinoid
- Intrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma
- Hemangiosarcoma
- Leiomyosarcoma
The liver is known as the silent organ, making it difficult to detect cancer in its early stages.
However, in advanced or terminal stages of liver cancer, symptoms such as loss of appetite, lethargy, ascites, and jaundice may appear.
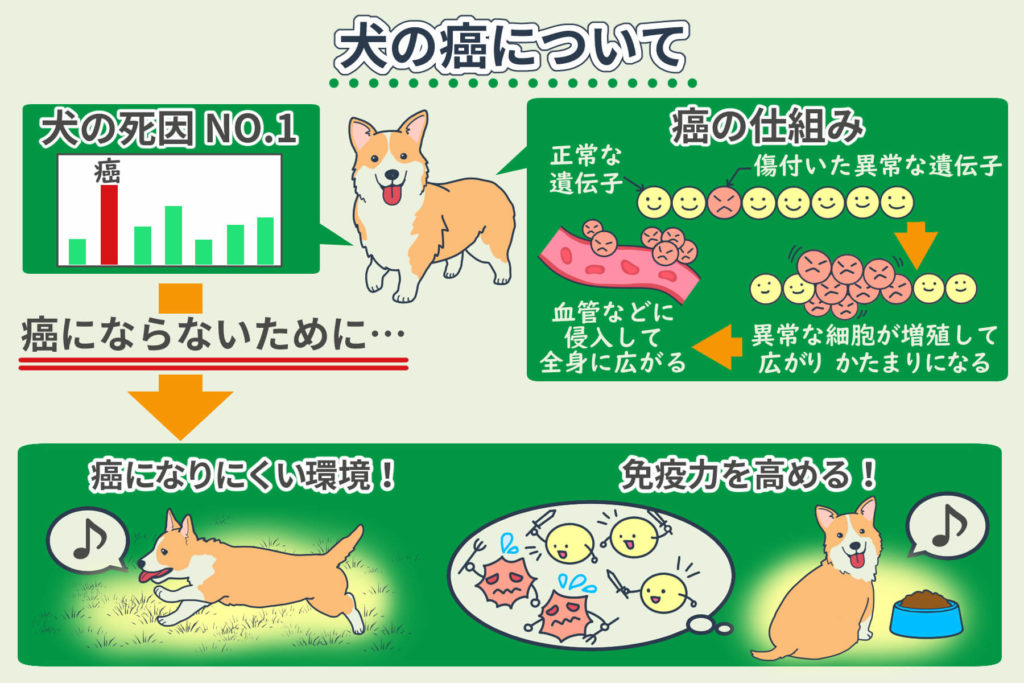
The 10 Causes of Cancer in Dogs
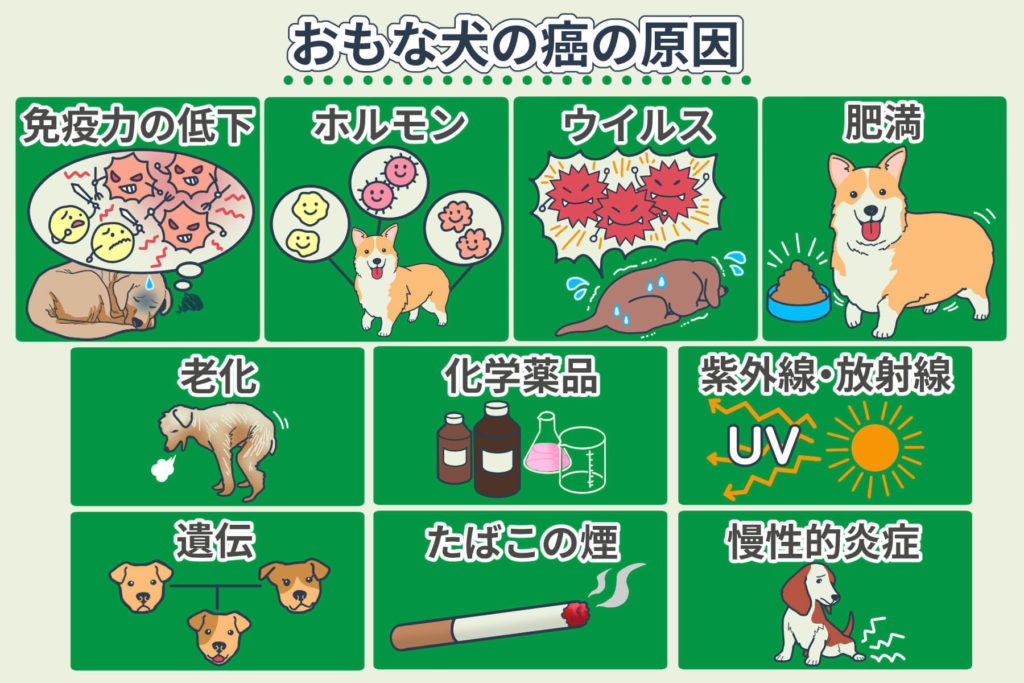
The primary causes of cancer in dogs include:
- Decreased immunity due to stress in dogs
- Aging in dogs
- Genetic factors and chemical agents (pesticides, herbicides, insecticides, food additives, etc.)
- Ultraviolet rays, radiation, tobacco smoke, chronic inflammation
- Hormonal factors (mammary gland tumors, perianal gland tumors, prostate cancer, etc.)
- Viruses
- Obesity in dogs
Decreased Immunity
Cancer and immunity in dogs are closely related.
It is unavoidable for errors (abnormalities) to occur in a dog’s cells due to various reasons.
Typically, even if abnormal cells occur in a dog’s body, the immune system detects, attacks, and eliminates these abnormal cells, preventing cancer from progressing.
However, if the immune system is compromised due to stress, aging, or other factors, it may fail to control the growth of the cancer, allowing it to grow visibly.
On the other hand, even if a dog has developed cancer, restoring immune function can help suppress the cancer.
Aging
Aging is a significant risk factor for cancer development in both dogs and humans.
One reason for the increased incidence of cancer in dogs is their longer average lifespan.
As dogs age, their immune system weakens, making it harder to detect, attack, and eliminate cancer cells, thereby increasing the likelihood of cancer.
It is recommended to incorporate immune support measures when your dog reaches middle to old age.
Genetics
Genetic factors are also a cause of cancer in dogs.
For example, some dogs are more prone to melanomas, and others to mammary gland tumors. Certain breeds are more susceptible to specific types of cancer.
However, in the case of cancer in dogs, acquired factors have a greater impact than congenital genetic factors. Therefore, please ensure to maintain a proper diet and living environment for them.
Chemicals
Chemicals, including pesticides, increase the incidence of cancer in dogs. Try to minimize the intake of such chemicals into their bodies.
Also, special attention is required when a cohabiting pet is undergoing anti-cancer drug treatment.
UV Rays & Radiation
It is believed that dogs exposed to strong UV rays or radiation are more likely to develop cancer.
It is advisable to avoid walking your dog during bright daylight and instead take them for walks in the early morning, evening, or night.
Tobacco Smoke (Secondhand Smoke)
While dogs do not smoke, they can develop cancer due to secondhand smoke if their family members smoke.
Tobacco smoke contains many carcinogens, so if you smoke, please make sure to do so away from your dog.
Chronic Inflammation
Chronic inflammation in dogs can stimulate cells and make it easier for cancer cells to develop.
Identify and eliminate the causes of inflammation, and give oils with anti-inflammatory effects like EPA and DHA appropriately to help reduce inflammation.
Hormones
Cancers such as mammary gland tumors (breast cancer) and prostate cancer are strongly influenced by hormones.
Neutering male dogs and spaying female dogs can prevent hormone-related diseases which often occur in middle-aged and older dogs, and statistically, it leads to longer lifespans.
Viruses
Chronic inflammation caused by viral infections, such as papillomavirus, can potentially lead to cancer in dogs.
Viruses can be eradicated if the immune system is functioning well, so always work to boost your dog’s immune system.
Obesity
Obesity in dogs can lead not only to cancer but also to various diseases like heart disease, arthritis, and diabetes.
A high carbohydrate intake can easily lead to obesity, so paying attention to their regular diet is crucial.
Five Cancer Treatments for Dogs
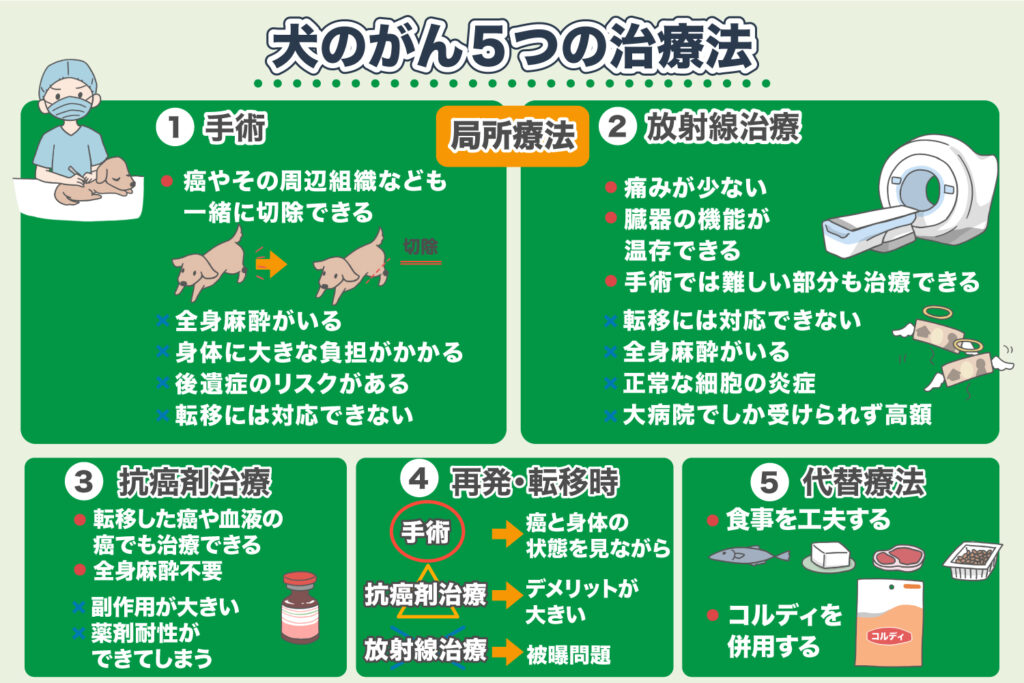
When a dog is diagnosed with cancer, it is common to undergo treatments such as “surgery and chemotherapy,” “steroids and antibiotics,” and in well-equipped hospitals, “radiation therapy.”
Surgery
The advantage of surgery is that it can simultaneously remove the cancer itself, the surrounding tissues, and any lymph nodes that have metastasized. This type of surgery to remove all cancer cells is called curative surgery.
### Surgery
Surgery is a treatment method that can potentially cure cancer if the cancer has not metastasized and remains localized (low invasiveness).
**Disadvantages of surgery for dogs include**:
– The necessity of general anesthesia,
– Significant physical stress due to the incision,
– The possibility of postoperative complications if the removed area results in loss of organ function.
Furthermore, if the cancer has spread, it becomes challenging to completely remove it through surgery.
### Radiation Therapy
Radiation therapy involves irradiating the cancer to destroy it.
Similar to surgery, radiation therapy is a local treatment that is effective when the cancer is localized. Unlike surgery, it is less painful because it does not involve incisions and makes it easier to preserve organ function. **It also has the advantage of being able to treat tumors located deep within the body or in the brain, where surgery might be difficult**.
However, **general anesthesia is required when a dog undergoes radiation therapy, which imposes some physical burden on the dog**.
**Disadvantages of radiation therapy include**:
– It is not suitable for metastatic cancer, similar to surgery,
– The need for general anesthesia,
– The potential for inflammation due to damage to healthy cells,
– Treatment availability is often limited to well-equipped hospitals like university hospitals,
– High costs associated with the treatment.
### Chemotherapy
The basic concept of chemotherapy is to kill cancer cells using strong toxins (chemotherapeutic agents).
**Advantages**:
– It can treat cancer that has metastasized,
– It can treat blood cancers,
– It does not require general anesthesia.
**Disadvantages**:
– Significant side effects,
– Potential bone marrow damage leading to decreased white blood cells and platelets, loss of appetite, vomiting, and overall decline in strength,
– Development of drug resistance limiting the effectiveness.
Some veterinarians may explain that “dogs are less prone to the side effects of chemotherapy,” but **dogs, just like humans, can experience side effects such as loss of appetite, fatigue, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and hair loss**.
Owners should carefully observe their dog during chemotherapy treatment and consult with their veterinarian if they notice any unusual behavior after treatment.
—
### Articles Related to Chemotherapy
### Treatment for Recurrence or Metastasis
Even if a dog undergoes surgery or radiation therapy to treat cancer, recurrence and metastasis are not uncommon.
Radiation therapy poses a challenge as the issue of exposure makes repeated treatments difficult. However, depending on the cancer’s state and overall health condition, another surgery may be considered.
If surgery or radiation therapy is not feasible, chemotherapy (including molecular targeted drugs like Palladia) might be suggested. Nonetheless, in many cases, the disadvantages (side effects) often outweigh the benefits (effects).
Aggressive treatment does not necessarily equate to treatment aimed at curing cancer. It is crucial to thoroughly discuss your beloved dog’s overall health, cancer condition, and the potential benefits and side effects of chemotherapy with your veterinarian before deciding whether or not to pursue chemotherapy.
Please note that not opting for chemotherapy does not equal neglect or lack of options. The following alternative therapies are approaches that can be started even if your dog has insufficient physical strength.
Alternative Therapies
While surgery, radiation therapy, and chemotherapy have their merits, they almost invariably lower immune system function and often diminish the Quality of Life (QOL).
Moreover, for advanced or terminal cancer cases where surgery is not an option, treatments that place a significant burden on the body can be challenging to perform.
However, many dogs maintain their QOL and sustain their vigor and appetite by incorporating dietary modifications and using supplements like Cordy. Therefore, even if your dog is diagnosed with advanced or terminal cancer and a limited prognosis, please don’t give up hope.
=> Things to Consider for Keeping Your Dog Smiling Despite a Cancer Diagnosis (Malignant Tumor)
Combating Cancer by Utilizing Immunity
Our proposal aims to enhance both physical strength and immunity without burdening your dog, thereby fighting cancer.
While we cannot guarantee results, this method is low-risk and tends to offer significant benefits.
The recommended steps are as follows:
- Limit carbohydrates to reduce glucose supply to cancer cells.
- Provide ample protein to build the physical strength necessary for a robust immune system.
- Administer Cordy, known for its results in improving cancer through immune enhancement.
Regarding Diet
Since diet is an everyday activity, it plays a crucial role in cancer prevention and is extremely important after a cancer diagnosis.
Cancer heavily consumes glucose for its growth, which is the principle behind PET-CT scans.
Reduce Glucose Intake
By reducing the amount of carbohydrates and sugars in daily meals and snacks, the glucose supply essential for cancer’s growth can be lowered, potentially inhibiting the cancer’s progression.
Rice, bread, noodles, and sweets are particularly high in carbohydrates, as are ingredients like potatoes and pumpkins. It is advisable to minimize their intake.
※ Note that even mixed grain rice contains high levels of carbohydrates, so caution is necessary.
While changing your dog’s diet alone may not cure cancer, it is crucial to implementing a certain degree of control to prevent cancer from growing uncontrollably.
We highly recommend checking the food labels (nutritional information) once again.
Since pet food is not required to display carbohydrate content, it is recommended to choose food with high protein content.
It’s advisable to select food with at least 30%, preferably 35%, protein per 100 grams.
Proactively Intake Essential Fatty Acids
Essential fatty acids are vital oils necessary for a dog’s survival.
Eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) are examples of these essential fatty acids.
These oils are crucial for cancer treatment involving inflammation, as they are expected to work on reducing inflammation.
We recommend blue fish like mackerel, saury, sardines, and mackerel, as well as salmon oil and Krill Oil.
Details About Dietary Therapy
Revising the diet is also important for improving cancer symptoms.
A low-carb, high-protein diet is highly recommended to help curb the progression of cancer.
We have compiled articles about dietary therapy for your reference, so please take a look.
- Dietary Therapy for Dogs and Cats with Cancer: Basics of High Protein, Low Carb
- New Dietary Ideas to Combat Cancer (Dogs and Cats Edition)
- Proactively Intake Vitamins for Cancer Countermeasures in Dogs and Cats
- BCAA Supplementation for Dogs and Cats with Declining Physical Strength, Liver, and Kidney Issues
- Healthy Gut! ~ Immunity Starts in the Gut ~ Recommendations for Gut Health and Probiotics
Proactively Addressing Immunity
Starting chemotherapy treatment will almost certainly lower physical strength and immunity.
If your dog’s physical strength and immunity decline, their quality of life (QOL) will drop. Even if treatment prolongs life slightly, it might only extend the time they suffer from cancer.
Therefore, to maintain physical strength and immunity, start with providing a good diet to build strength so they won’t have to abandon treatment due to side effects.
Make sure not to let their immunity decline.
Originally, immunity is the main agent in suppressing cancer, and chemotherapy acts merely as an aid.
By proactively utilizing alternative therapies, dietary therapy, and Cordyceps, we aim to improve prognoses through immunity measures.
We believe in harnessing the best aspects of various treatments. Relying solely on chemotherapy is clearly insufficient.
It is essential to combine complementary treatments.
For a Treatment Free of Regret
We have compiled information that pet owners whose dogs have been diagnosed with cancer should know first and foremost.
The content here is based on knowledge and ideas gathered from exchanges with advanced veterinarians and pet owners.
We never impose our views.
It’s natural for there to be a variety of perspectives and decisions.
We don’t want the owners to have any regrets. We don’t want you to regret your choices later on.
Should you proceed with treatment or not?
Surgery or chemotherapy?
There is no correct answer to these questions when it comes to cancer treatment.
Conversely, we can say this:
Any choice made by the owner out of love for their dog is the right choice.
We want you to understand the realities of cancer treatment to help you make better choices.
You don’t need to memorize every detail or test result.
However, we want you to know that there are many things you can do at home and as a family, without relying solely on surgery, chemotherapy, or leaving everything to the veterinarian.
Cordy, which has potential immunomodulatory functions, may help suppress tumor growth and prevent recurrence.
While it is uncertain how much response or improvement can be expected, there is a significant possibility that at the very least, your pet will regain appetite and energy.
When using medications like chemotherapy, steroids, or antibiotics, liver function decline is a concern.
In such cases, using domestically produced SPF-derived porcine placenta powder in conjunction may help minimize liver damage.
Even in cases where liver values have already worsened, domestically-produced SPF-derived porcine placenta powder can improve liver function within about a month in many instances.
Furthermore, since tumors, cancer, and sarcomas often involve severe inflammation, it seems effective to give Krill Oil extracted from Antarctic shrimp containing EPA/DHA, which has expected anti-inflammatory effects.
Our lab continues research on Cordy, which has expected immunomodulatory effects, domestically-produced SPF-derived porcine placenta powder, which is expected to protect liver function, and Krill Oil, which is expected to have anti-inflammatory effects. If you have any questions, please feel free to contact us.
There are also many case studies and improvement examples available for you to see.
Feel free to consult us at any time.
監修獣医師:林美彩 所属クリニック:chicoどうぶつ診療所

代替療法と西洋医学、両方の動物病院での勤務経験と多数のコルディの臨床経験をもつ。 モノリス在籍時には、一般的な動物医療(西洋医学)だけでは対応が困難な症例に対して多くの相談を受け、免疫の大切さを痛烈に実感する。
ペットたちの健康維持・改善のためには薬に頼った対処療法だけではなく、「普段の生活環境や食事を見直し、自宅でさまざまなケアを取り入れることで免疫力を維持し、病気にならない体づくりを目指していくことが大切である」という考えを提唱し普及活動に従事している。
所属: